Hover on images to see descriptions.
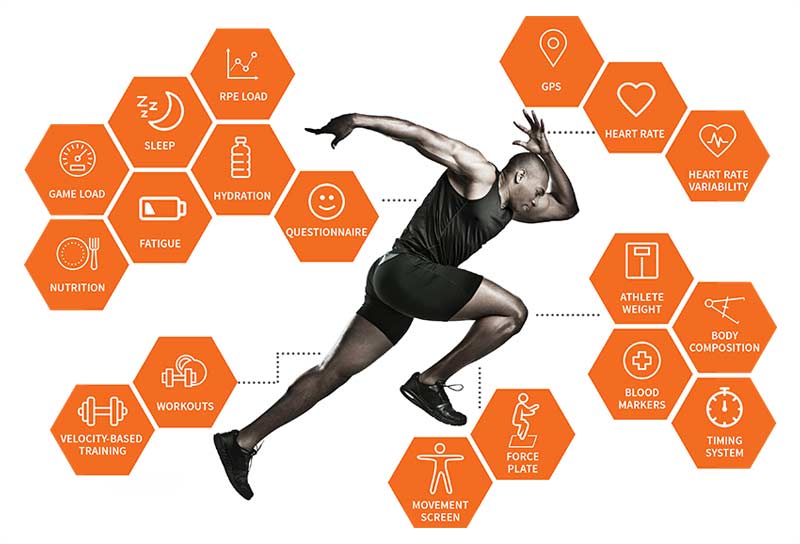
Many coaches and athletes are showing an increasing interest in training monitoring systems every year. There is a plethora of performance markers that can aid in a coaches assessment of physiological and psychological conditions of their athletes. These markers can indicate an athlete’s readiness for competition, adaptation to training, or risk for injury. However, studies have shown examination of these performance markers individually may not result in a clear perception of one’s performance. Hence, an inclusive analysis of these metrics is required to achieve meaningful assessment. This projects involves a novel athletic monitoring system and predictive analysis tool on athletic condition.
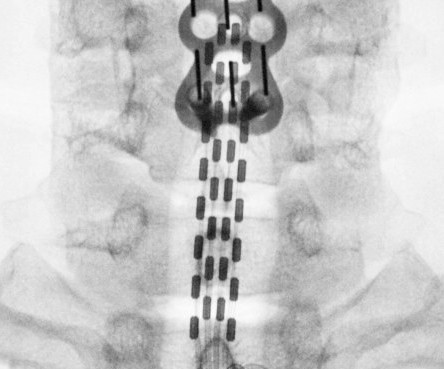
Choosing the optimal epidural stimulation variables, such as the frequency, intensity, and location of the stimulation, significantly affects maximal motor functionality. This project suggests a novel technique using machine learning methods to maximize the functionality of a SCI patients after epidural stimulation.
In this project a humanoid robot is used to increase the effectiveness of rehabilitation procedures. We have developed method based on machine learning and computer vision to operate a robot that helps a user to understand and follow a set of clinically recommended activities.

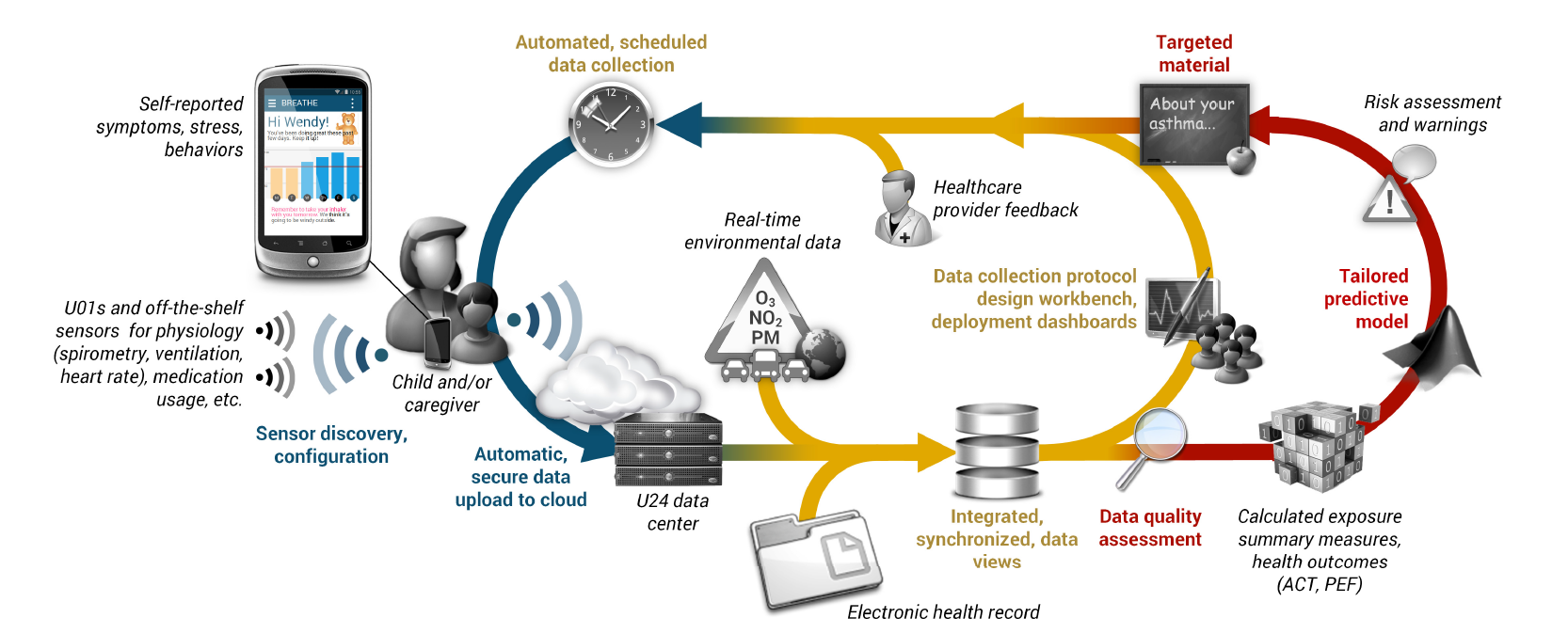
BREATHE aims to be the leader in the development and application of mobile health technologies that deepen our scientific understanding and clinical management of pediatric conditions by proposing the creation of an innovative end-to-end software infrastructure for sensor-based pediatric asthma monitoring. Our vision and proposed research are motivated by the following question, what if you could predict ahead of time, for a specific asthma patient, the potential for exacerbation and thus mitigate (if not prevent) the event?
Current mechanisms for screening and identifying patients at risk for severe mental health crises, including suicide attempts, have limited predictive success. Compounding this issue is that many individuals who would most need mental health interventions during crisis moments fail to reach out to professionals to receive help. The result is that many of the most vulnerable individuals fail to receive the care they need most. This project explores the potential of smart devices to collect passive sensing data that can interpret an individual's mental state, and detect the potential onset of a mental health crisis.

Alzheimer's disease and other dementias in the geriatric population are the leading cause of death in the United States. In 2017, the healthcare cost of dementia is estimated more than $259 billion. An early diagnosis and keeping the brain healthy enables prevention of cognitive impairment. We are assessing physiological characteristics and physical activity from people who have been diagnosed with a memory problem, brain disorder, and/or dementia collaborating the study with Department of Neurology and Psychiatry at UCLA. We are developing a non-invasive and wireless transmission system and analyzing multiple factors to characterize cognitive impairment in the older adult.

WLA in india face profound challenges in acessing treatment regiments and medications. This project aims to provide a remote health monitoring system to evaluate the impact of Accredited Social Work Activists support, nutrition training and food supplementation on physical and health condition, of the WLA and their children over a period of time.

In real-world scenarios, different features have different acquisition costs at test-time which necessitates cost-aware methods to optimize the cost and performance trade-off. This paper introduces a novel and scalable approach for cost-aware feature acquisition at test-time. The method incrementally asks for features based on the available context that are known feature values. The proposed method is based on sensitivity analysis in neural networks and density estimation using denoising autoencoders with binary representation layers.
Recent studies suggest that epidural stimulation of the spinal cord could increase the motor pattern both in motor and sensory complete spinal cord injury (SCI) patients. This paper presents a novel technique using machine learning methods to predict the functionality of a SCI patient after epidural stimulation.
To address the need for asthma self-management in pediatrics, we present the feasibility of a mobile health (mHealth) platform built on their prior work in an asthmatic adult and child.







